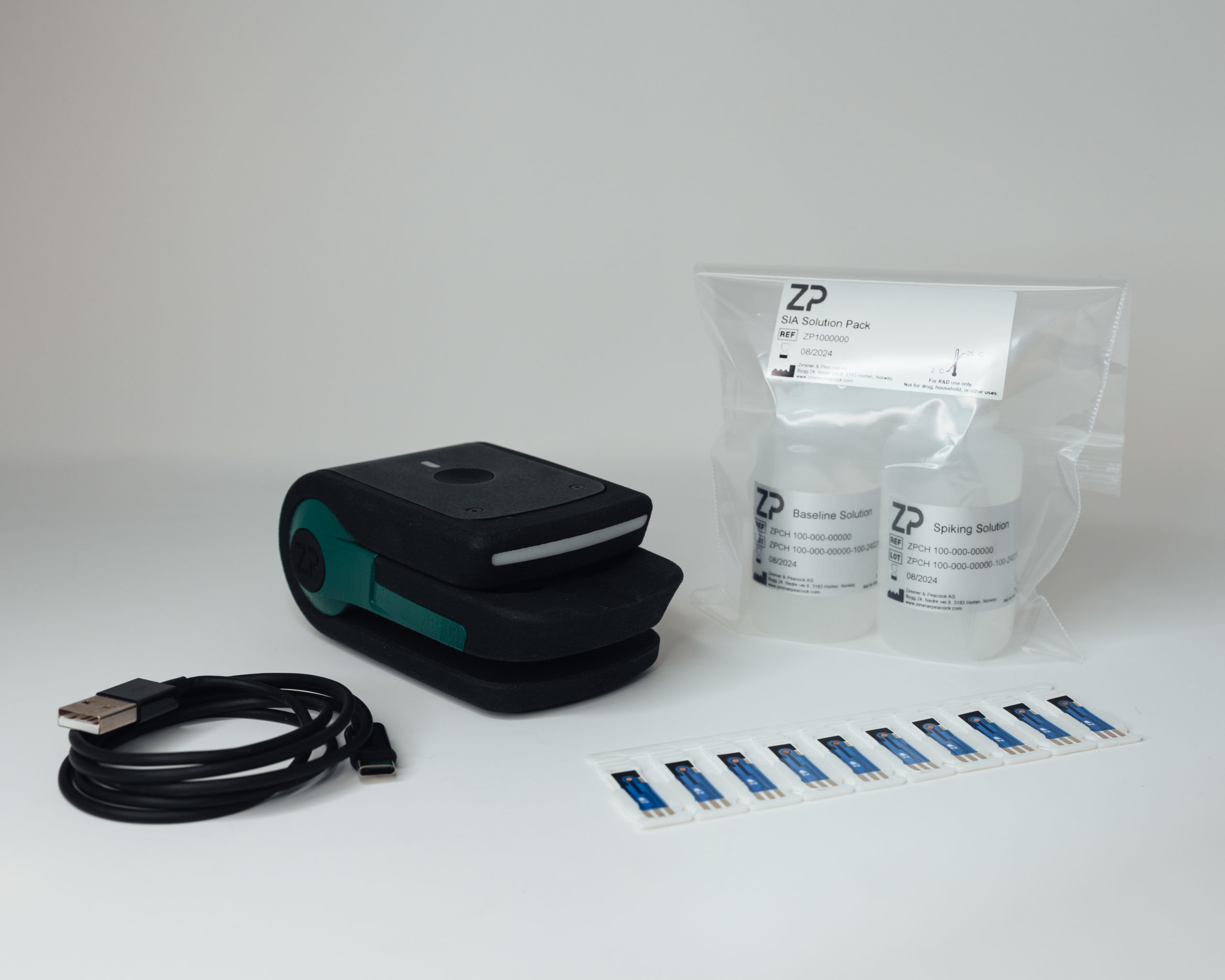
ZP has lauched a revolution in potentiostat, app drive, Cloud connected with a complete data tunnel built into the system from raw signal to analyte concentration.
Technologies covered included:

Key Points
- Wastewater-Based Epidemiology (WBE): The webinar focused on the potential of WBE as a tool for early disease detection and monitoring.
- Challenges in WBE: Current WBE methods often involve complex, time-consuming processes, hindering rapid response to outbreaks.
- Inspiration from Other Industries: The speaker drew parallels between WBE and other fields like diabetes management and food testing.
- Electrochemical Sensors: These sensors, similar to those used in glucose meters, offer a promising solution for rapid and low-cost WBE analysis.
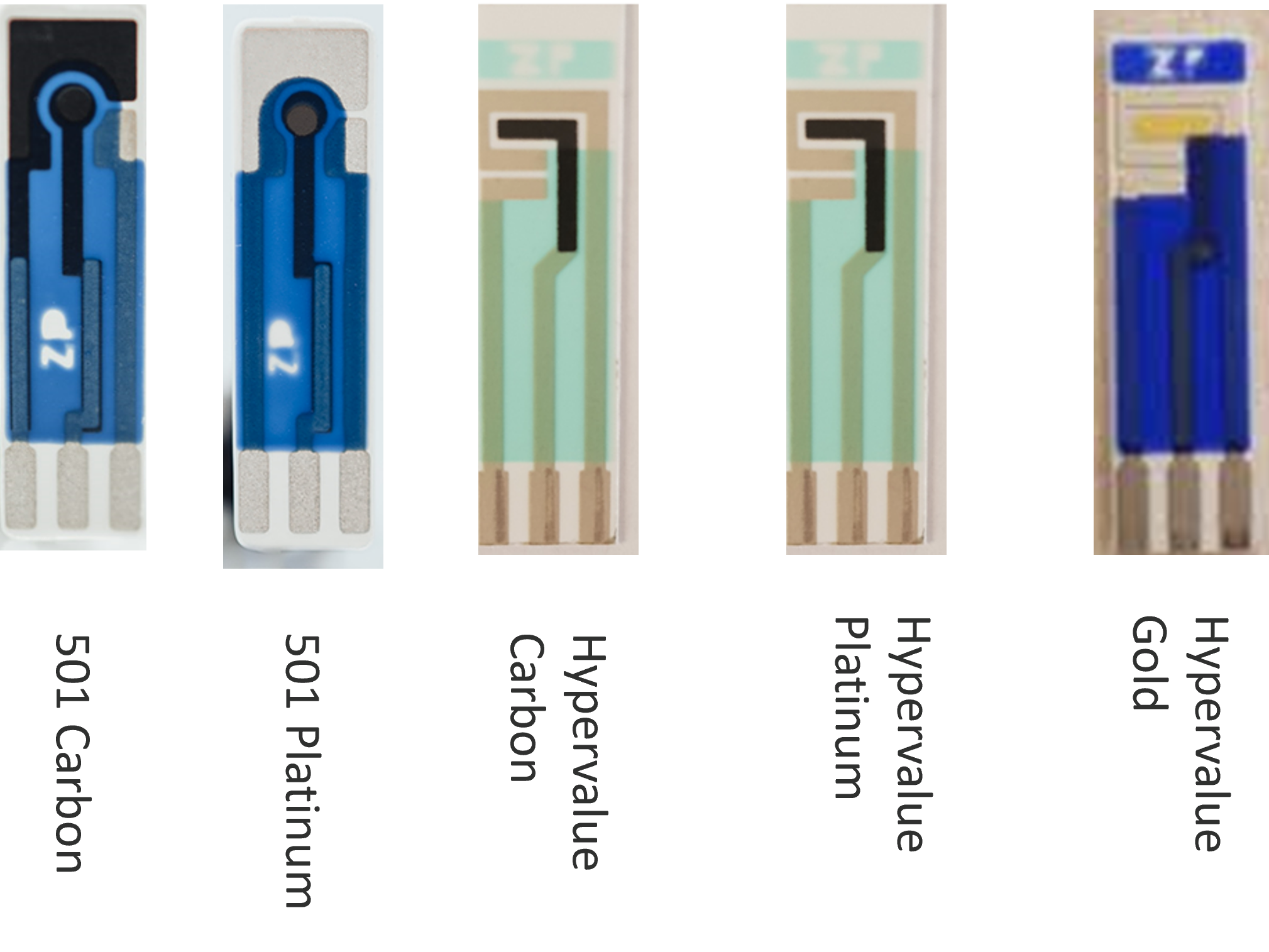
- Platform Approach: The speaker’s company, zp, has developed a versatile platform that can be adapted to detect various analytes in water samples through simple sensor swaps.
- Benefits of Electrochemical Sensors:
- Rapid analysis
- Low cost
- Minimal sample preparation
- Potential for decentralized testing
Core Argument
By applying the principles and technology used in glucose monitoring to wastewater analysis, it’s possible to significantly improve the speed, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility of WBE. This could lead to earlier detection of disease outbreaks and more effective public health interventions.
Potential Applications
- Monitoring for pathogens like poliovirus
- Tracking the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
- Detecting emerging contaminants in water bodies
- Assessing the effectiveness of public health interventions
Overall
The webinar presented a compelling case for the use of electrochemical sensors in WBE. By highlighting the successes of this technology in other fields, the speaker effectively demonstrated its potential to revolutionize water quality monitoring and public health surveillance.
